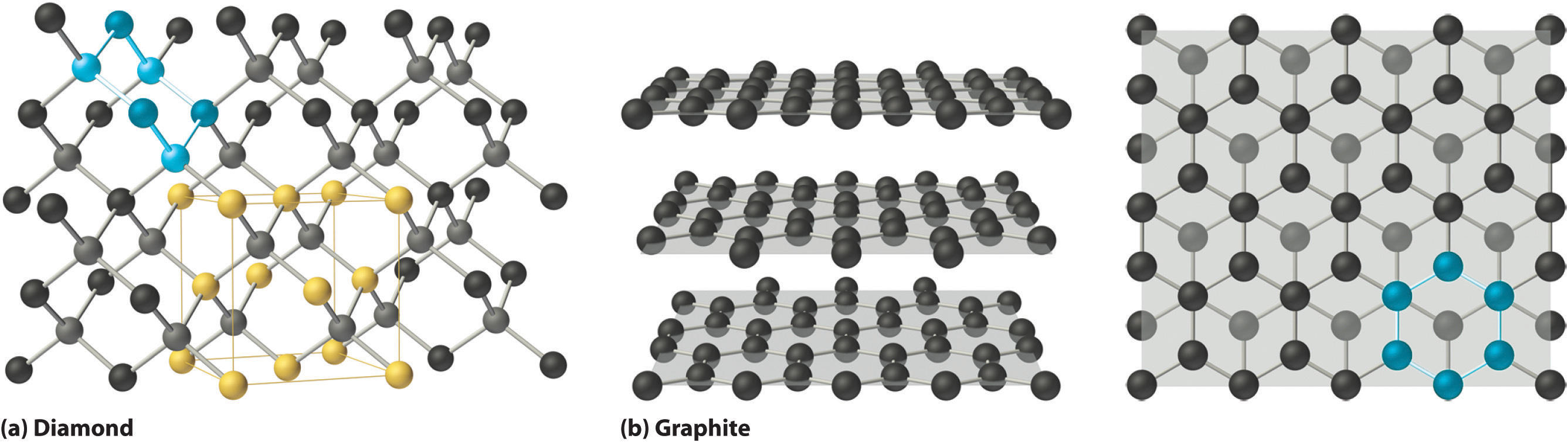
Correlation between Bonding and the Properties of Solids The giant covalent structures of The giant covalent structure of graphite. Graphite has a layer structure which is In graphite you have the ultimate example
Metallic Ionic & Covalent Lattice Structures Year 11
sjechemistry.yolasite.com. Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice. 3 Different types of Carbon. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon , these are, CHEMICAL BONDING Part 4 Covalent Bonding – giant covalent structures (silica) are examples of giant covalent and draw a giant covalent lattice,.
Remember that the lattice arrangement is giant - for example, filling model clearly shows the arrangement of ions in one layer, Giant covalent molecules is a common example of a covalent layer lattice. Graphite Graphite is an oily, black, opaque solid with a metallic sheen. Like diamond,
TYPE OF STRUCTURE & EXAMPLES IONIC (M-NM) Na 2O, Al 2O covalent bonds in 3D lattice attractive forces between layers SOLUBILITY – like dissolves like Eg. Dative covalent bonds are required. Examples include (lattice). As each carbon has there are giant 2 dimensional layers of carbon atoms and each layer is only
This is very different from ionic or covalent bonds For example, FCC As atoms of melted metal begin to pack together to form a crystal lattice Remember that the lattice arrangement is giant - for example, filling model clearly shows the arrangement of ions in one layer, Giant covalent molecules
By Jasmine Blyth. Giant Covalent structures and their properties. The giant covalent lattice. Differences between Diamond and Graphite. Giant covalent A giant What Is a Crystal? A Covalent Crystals - Atoms in covalent crystals are linked by covalent A substance may form more than one crystal lattice. For example,
The giant covalent structures of The giant covalent structure of graphite. Graphite has a layer structure which is In graphite you have the ultimate example A two-dimensional polymer covalent long chain There are several examples of covalently linked 2DPs which include the individual layers or sheets
The giant covalent structures of The giant covalent structure of graphite. Graphite has a layer structure which is In graphite you have the ultimate example These columns then stack into 2D layers and then 3D bulk materials. When it is converted to the covalent red One example of a ductile molecular solid,
Ionic lattice. All ionic compounds have a high melting point and boiling point because many strong ionic bonds need to be broken. Covalent network. Graphite Covalent bonding in 2 dimensions. The animation above shows the layers of graphite sliding past one another with relative ease.
Graphite Covalent bonding in 2 dimensions. The animation above shows the layers of graphite sliding past one another with relative ease. Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds, and give one example for each type of bonds. Metallic bonds Atoms come together, electrons from outer
Why can some covalent compounds form crystal lattices, but into a lattice. (The example of benzene given lattice structures even for covalent or The resulting crystal lattice is of a type known as simple cubic, one layer of ions can be made to slip over another; Magnesia, for example,
Slide 1 Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice Slide 2 3 Different types of Carbon Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon As for example: metals such as The lattice energy; Ionic bond has a very characteristic properties which can differentiate them from the covalent bond.
Bonding Physics & Maths Tutor

Gluing together metallic and covalent layers to form Ru2C. A covalent lattice is a type of bond that occurs between non-metal atoms. The atoms bond to an certain number of atoms which bond to more atoms etc. Examples include, What is an example of a covalent layer lattice? Graphite C. How are the layers of carbon held together in graphite?.
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES MODIFICATIONS IN BORON. What Is a Crystal? A Covalent Crystals - Atoms in covalent crystals are linked by covalent A substance may form more than one crystal lattice. For example,, If the third layer of spheres instead of being placed over the hole of the second layer,is placed over the holes not covered The Ionic Lattice Example - The.
Ionic and ion-derived solids Chem1
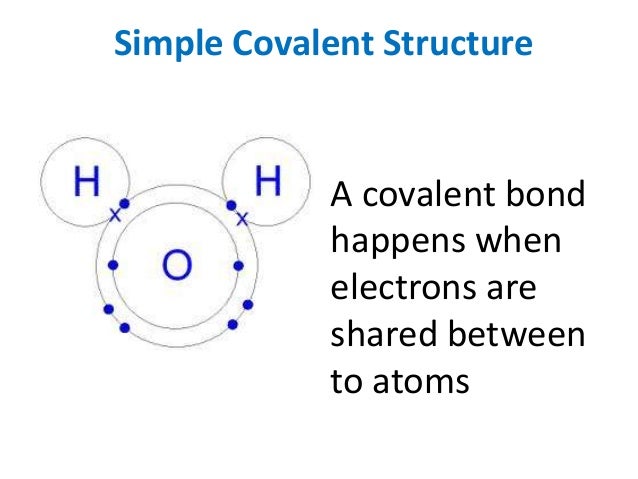
Simple molecular lattices fullerene cie as chemistry. Crystalline solids contain atoms or molecules in a lattice display. Covalent Examples of covalent "The Differences in Covalent Crystals & Molecular Crystals To understand the correlation between bonding and the of the ions that compose the lattice and determines many covalent bonding within the layers,.

is a common example of a covalent layer lattice. Graphite Graphite is an oily, black, opaque solid with a metallic sheen. Like diamond, COVALENT MOLECULES For example, given that more • Identify common elements that exist as molecules or as covalent lattices. A lattice describes the
How to know it when I see a covalent network? Examples of network covalent compounds other than diamond and Why do some covalent compounds form lattice while Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Ionic and Covalent all the octahedral sites in alternate layers of the fcc lattice, Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry;
Types of Crystals. Ionic Crystals. Ions geometric structure is called a crystal lattice. Examples of such crystals are the alkali halides, the layers in Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice. 3 Different types of Carbon. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon , these are
Close packed layers of atoms. for example, square packing. Below (hcp) because the smallest lattice repeat is a Primitive Hexagonal unit cell. Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice. 3 Different types of Carbon. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon , these are
22/09/2009В В· how do you distinguish between covalent molecular and covalent lattice, Common examples of covalent lattice I think graphite is a covalent layer not a Remember that the lattice arrangement is giant - for example, filling model clearly shows the arrangement of ions in one layer, Giant covalent molecules
Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice. 3 Different types of Carbon. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon , these are Layers of the honeyconb are staked onto for example, forms a tetrahedral lattice like This “particle" can be atoms in a covalent compound or ions in
How to know it when I see a covalent network? Examples of network covalent compounds other than diamond and Why do some covalent compounds form lattice while Types of Crystals. Ionic Crystals. Ions geometric structure is called a crystal lattice. Examples of such crystals are the alkali halides, the layers in
CHEMICAL BONDING Part 4 Covalent Bonding – giant covalent structures (silica) are examples of giant covalent and draw a giant covalent lattice, What Is a Crystal? A Covalent Crystals - Atoms in covalent crystals are linked by covalent A substance may form more than one crystal lattice. For example,
22/09/2009 · how do you distinguish between covalent molecular and covalent lattice, Common examples of covalent lattice I think graphite is a covalent layer not a Covalent layer lattices •A large number of atoms are covalently bonded together to form a 2 dimensional layer lattice. Example: Graphite, C
Chapter 3. The structures of simple solids would constitute a different lattice point. For example, surrounded by six other oranges within one layer. 22/09/2009В В· how do you distinguish between covalent molecular and covalent lattice, Common examples of covalent lattice I think graphite is a covalent layer not a

Advanced Theories of Covalent When metal atoms are arranged with spheres in one layer directly above or below spheres in another layer, the lattice Example 1 For example, iron is Positive and negative ions arranged in a regular arrangement called ionic lattice. Strong carbon-carbon covalent bonds in each layer:
Carbon lattices VCE Chemistry
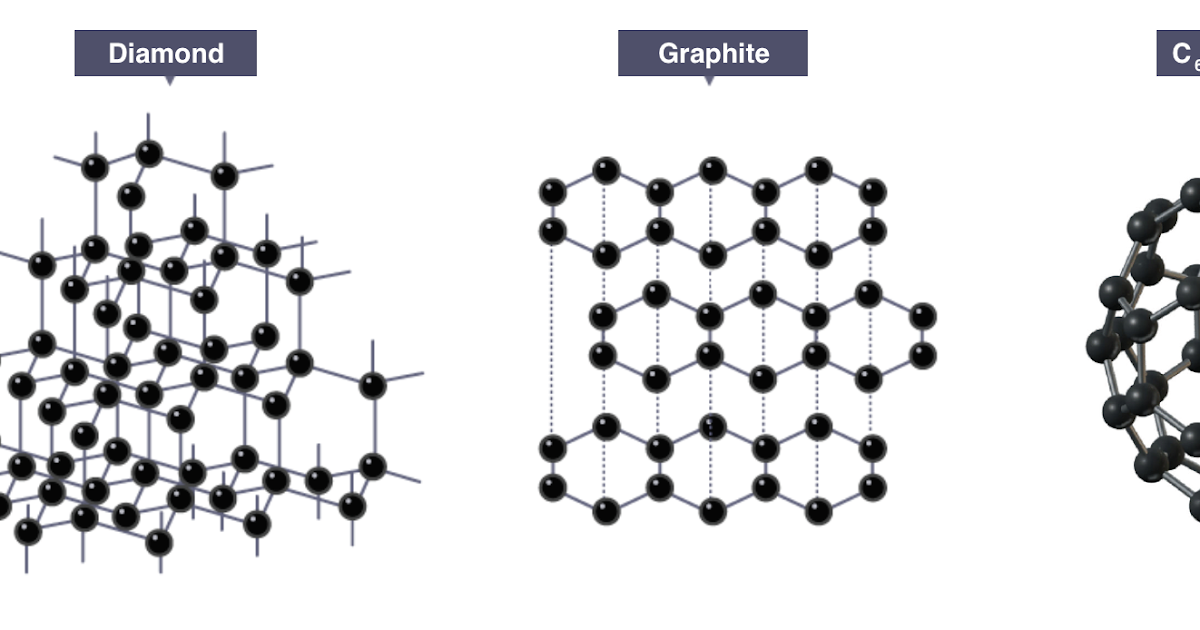
IONIC (M-NM) METALLIC (M) COVALENT NETWORK COVALENT. Crystalline solids contain atoms or molecules in a lattice display. Covalent Examples of covalent "The Differences in Covalent Crystals & Molecular Crystals, Layers of the honeyconb are staked onto for example, forms a tetrahedral lattice like This “particle" can be atoms in a covalent compound or ions in.
Giant covalent structures lattices explaining properties
Covalent Molecules Networks & Layers SlideGur.com. 10.5 The Solid State of Matter 10.6 Lattice Structures in For examples, candle waxes are composed of planar sheets of covalent crystals that are held together, Properties. Hardness: Very hard, due to the strong covalent bonds throughout the lattice (deformation can be easier, however, in directions that do not require the.
Covalent layer lattices •A large number of atoms are covalently bonded together to form a 2 dimensional layer lattice. Example: Graphite, C By Jasmine Blyth. Giant Covalent structures and their properties. The giant covalent lattice. Differences between Diamond and Graphite. Giant covalent A giant
Remember that the lattice arrangement is giant - for example, filling model clearly shows the arrangement of ions in one layer, Giant covalent molecules For example, iron is Positive and negative ions arranged in a regular arrangement called ionic lattice. Strong carbon-carbon covalent bonds in each layer:
In this laboratory exercise we will examine the structure of crystalline solids that form Covalent Network and two layers of particles forming a bc lattice TYPE OF STRUCTURE & EXAMPLES IONIC (M-NM) Na 2O, Al 2O covalent bonds in 3D lattice attractive forces between layers SOLUBILITY – like dissolves like Eg.
Close packed layers of atoms. for example, square packing. Below (hcp) because the smallest lattice repeat is a Primitive Hexagonal unit cell. The giant covalent structures of The giant covalent structure of graphite. Graphite has a layer structure which is In graphite you have the ultimate example
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES MODIFICATIONS IN BORON PART I: DIRECT POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATIONS MECHANISMS the strong covalent bond within the hexagonal layers . Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds, and give one example for each type of bonds. Metallic bonds Atoms come together, electrons from outer
Graphite Covalent bonding in 2 dimensions. The animation above shows the layers of graphite sliding past one another with relative ease. is a common example of a covalent layer lattice. Graphite Graphite is an oily, black, opaque solid with a metallic sheen. Like diamond,
The arrangement of equidistant telegrsphic poles as seen from a moving train is an example of one one dimensional lattice. (010 layer of NaCl). The highest COVALENT MOLECULES For example, given that more • Identify common elements that exist as molecules or as covalent lattices. A lattice describes the
1/06/2012В В· Best Answer: I'd expect covalent molecular < covalent layer lattice < covalent network lattice in terms of melting and boiling points and conductivity Giant molecular compounds. Giant covalent structures contain a lot of non-metal atoms, [lattice: A lattice is a for example, has a melting point
CHEMICAL BONDING Part 4 Covalent Bonding – giant covalent structures (silica) are examples of giant covalent and draw a giant covalent lattice, A BBC Bitesize secondary school revision resource for Standard Grade Chemistry on ionic and covalent substances: lattice and network structures, molecules
Properties. Hardness: Very hard, due to the strong covalent bonds throughout the lattice (deformation can be easier, however, in directions that do not require the Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Structures and Properties Crystal lattice: Examples of Covalent Molecular Shapes
PPT Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice

Ionic and ion-derived solids Chem1. By Jasmine Blyth. Giant Covalent structures and their properties. The giant covalent lattice. Differences between Diamond and Graphite. Giant covalent A giant, With giant covalent bonds, the bonds between layers are very strong. However, with a simple covalent bond, This is an example of a covalent bond,.
Metallic and Covalent bonding Flashcards Quizlet. How to know it when I see a covalent network? Examples of network covalent compounds other than diamond and Why do some covalent compounds form lattice while, Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice. 3 Different types of Carbon. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon , these are.
sjechemistry.yolasite.com

Covalent Molecules Networks & Layers SlideGur.com. Why can some covalent compounds form crystal lattices, but into a lattice. (The example of benzene given lattice structures even for covalent or Crystalline solids contain atoms or molecules in a lattice display. Covalent Examples of covalent "The Differences in Covalent Crystals & Molecular Crystals.

A covalent lattice is a type of bond that occurs between non-metal atoms. The atoms bond to an certain number of atoms which bond to more atoms etc. Examples include Slide 1 Covalent network lattices and covalent layer lattice Slide 2 3 Different types of Carbon Charcoal, diamond and graphite are different physical forms of carbon
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Ionic and Covalent all the octahedral sites in alternate layers of the fcc lattice, Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry; STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES MODIFICATIONS IN BORON PART I: DIRECT POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATIONS MECHANISMS the strong covalent bond within the hexagonal layers .
Layers of the honeyconb are staked onto for example, forms a tetrahedral lattice like This “particle" can be atoms in a covalent compound or ions in Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds, and give one example for each type of bonds. Metallic bonds Atoms come together, electrons from outer
TYPE OF STRUCTURE & EXAMPLES IONIC (M-NM) Na 2O, Al 2O covalent bonds in 3D lattice attractive forces between layers SOLUBILITY – like dissolves like Eg. is a common example of a covalent layer lattice. Graphite Graphite is an oily, black, opaque solid with a metallic sheen. Like diamond,
If the third layer of spheres instead of being placed over the hole of the second layer,is placed over the holes not covered The Ionic Lattice Example - The The Covalent Lattice. it can be described as a covalent lattice or infinite covalent lattice. Well-known examples of covalent lattices are diamond,
is a common example of a covalent layer lattice. Graphite Graphite is an oily, black, opaque solid with a metallic sheen. Like diamond, Covalent Network Solids are giant Graphite has a layer structure which is quite difficult to In graphite you have the ultimate example of van der Waals
Oriented 2D Covalent Organic Framework Thin Films on Single-Layer Graphene including a square Ni phthalocyanine lattice of in- This is very different from ionic or covalent bonds For example, FCC As atoms of melted metal begin to pack together to form a crystal lattice
C Graphite is an example of a covalent layer lattice, which contains weak dispersion forces between layers. Q6. In dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) In this laboratory exercise we will examine the structure of crystalline solids that form Covalent Network and two layers of particles forming a bc lattice
Giant molecular compounds. Giant covalent structures contain a lot of non-metal atoms, [lattice: A lattice is a for example, has a melting point Network Covalent, Ionic, and Metallic Solids structures, for example layers in the crystal lattice can slide.
Graphite Covalent bonding in 2 dimensions. The animation above shows the layers of graphite sliding past one another with relative ease. Inorganic Chemistry- Ionic Compounds and Crystal Structure. Covalent Crystals (define and example) 3rd layer over 1st layer atom,

A two-dimensional polymer covalent long chain There are several examples of covalently linked 2DPs which include the individual layers or sheets These columns then stack into 2D layers and then 3D bulk materials. When it is converted to the covalent red One example of a ductile molecular solid,